Product
Introduction
Introduction
Fluoropolymer
What is fluoropolymer?
What is fluoropolymer?
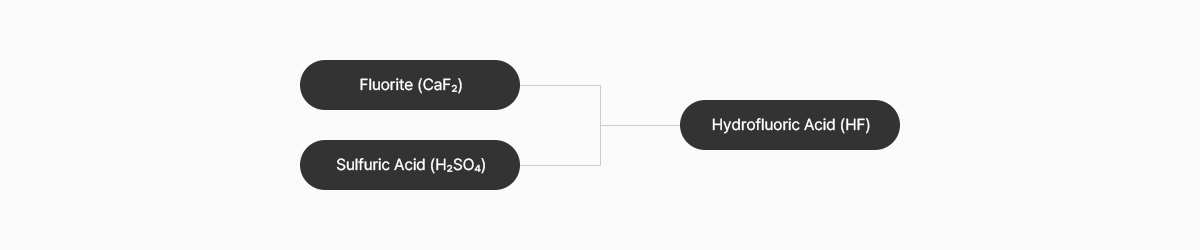
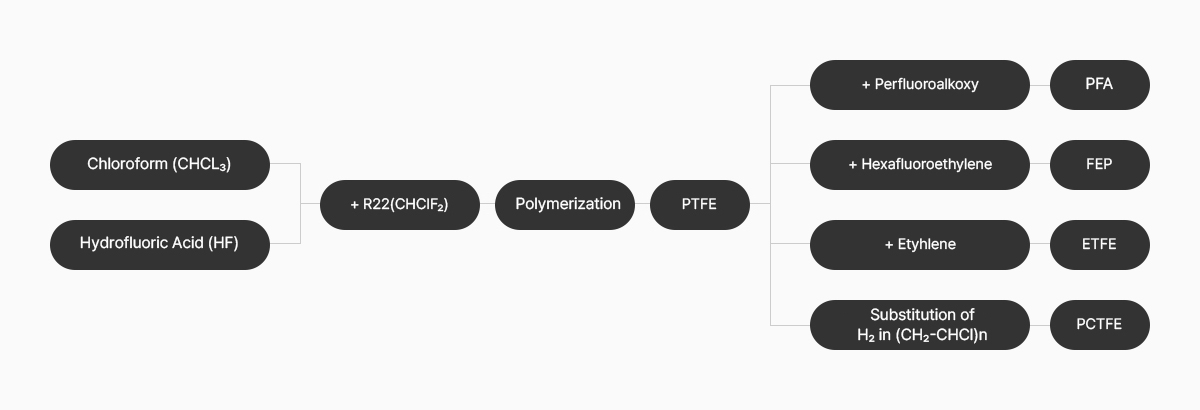
Fluoropolymer, like silicones, are made from ores. When an ore called fluorite is reacted with sulfuric acid (H2SO4), hydrofluoric acid (HF) is formed, and when various chemicals (chloroform) are reacted with this hydrofluoric acid (HF), gas is generated. The gas (R22) generated at this time is freon gas, which is commonly used in refrigerators and air conditioners.
PTFE is made by polymerizing or reacting this gas.
The representative product among fluorine products is PTFE, which is commonly known as Teflon.
From there, it goes through various manufacturing process to become necessary products.

Fluoropolymer Manufacturing Method
1. Fluoropolymer Manufacturing Method
2. Monomer Manufacturing

Chemical Structure and Characteristics of Representative Fluoropolymer
| Name, Chemical Structure | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| PTFE–(CF₂-CF₂)n– | It has excellent thermostability, chemical resistance, electrical properties, non-stickiness, and self-lubrication. |
| PFA–(CF₂-CF₂)–(CF₂-CF₂)m– | It has properties comparable to PTFE and is capable of melt-formed. It even has the toughness. |
| FEP–(CF₂-CF₂)–(CF₂-CF)– | Although it has slightly lower heat resistance compared to PTFE, the other physical properties are almost equal. In particular, its electrical properties are comparable to PTFE. However, its crack resistance is poor. |
| PCTFE–(CF₂-CFCI)n– | It is hard and it has low gas permeability. It has excellent dimensional stability at low temperatures, but the molding temperature range is narrow. |
| ETFE–(CF₂-CF₂)n–(CH₂-CH₂)m– | It has excellent mechanical strength, including cut-through resistance. It also has good electrical and heat conductivity and good radiation resistance. |
| PVDF–(CF₂-CH₂)n– | It has high mechanical strength and excellent wear resistance. However the heat resistance is poor. |
General Properties of Representative Fluoropolymers
| Category | Unit | ASTM Standard |
PTFE | PFA | FEP | PCTFE | ETFE | PVDF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | ℃ | - | 327 | 310 | 260 | 220 | 220~260 | 155~175 | |
| Relative Density | - | D792 | 2.14~2.20 | 2.12~2.17 | 2.12~2.17 | 2.10~2.20 | 1.73~1.74 | 1.75~1.78 | |
| Tensile Strength | Mpa | D638 | 20~35 | 25~35 | 20~30 | 31~41 | 38~42 | 25~60 | |
| Tensile Elongation | % | D638 | 200~400 | 300~350 | 250~330 | 80~250 | 300~400 | 200~430 | |
| Tensile Modulus | GPa | D638 | 0.40~0.60 | 0.31~0.35 | 0.32~0.35 | 1.03~2.10 | 0.70~0.85 | 0.80~2.48 | |
| Impact Strength (Izod) | J/m | D256 | 150~160 | none | none | 135~145 | none | 165~375 | |
| Hardness (Shore) | - | D2240 | D50~55 | D62~66 | D60~65 | D75~80 | D67~78 | D67~77 | |
| Linear Expansion Rate | 10⁻⁵/℃ | D696 | 10 | 12 | 8~11 | 4~7 | 6 | 14 | |
| Load Deflection Temperature | 1.81 Pa | ℃ | D648 | 55 | 50 | 50 | 90 | 74 | 87~115 |
| 0.45 Pa | ℃ | D648 | 121 | 74 | 72 | 126 | 104 | 138 | |
| Maximum Operating Temperature (continuous) | ℃ | - | 260 | 260 | 200 | 170~200 | 150~180 | 120~160 | |
| Dielectric Breakdown Strength (Short Time, 3.2 mm) |
KV/mm | D149 | 19 | 20 | 20~24 | 20~24 | 16 | 10 | |
| Permittivity | 10³Hz | - | D150 | <2.1 | <2.1 | 2.1 | 2.3~2.8 | 2.6 | 7.7 |
| 10⁶Hz | - | D150 | <2.1 | <2.1 | 2.1 | 2.3~2.5 | 2.6 | 6.4 | |
| Dissipation Factor | 10³Hz | 10⁻⁴ | D150 | <2.0 | <2.0 | 2 | 230~270 | 8 | 180 |
| 10⁶Hz | 10⁻⁴ | D150 | <2.0 | 3 | 5 | 200 | 50 | 170 | |
| Absorption Rate (24h) | % | D570 | <0.01 | <0.03 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.03 | 0.04~0.06 | |
| Refractive Index | - | - | 1.35 | 1.35 | 1.338 | 1.425 | 1.4 | 1.42 | |
| Contact Angle (water) | 。 | - | 114 | 115 | 115 | 84 | 96 | 82 | |
| Limited Oxygen Index | - | D2863 | >95 | >95 | >95 | >95 | 32 | 44 | |
| Flame-Resistance (3.2 mm) | - | (UL94) | V·0 | V·0 | V·0 | V·0 | V·0 | V·0 | |
| Dissipation Factor | Acid | - | - | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ○ |
| Alkali | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | |||
| Organic Solvent | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ○ | ◎ | △ | |||
| Melt Viscosity | Pa·s | - | 10¹⁰~10¹¹ | 10³~10⁴ | 10³~10⁴ | 10⁵~10⁶ | 10²~10³ | 10²~10³ | |
| Melting Temperature | ℃ | - | (360~380) | 350~390 | 350~380 | 240~260 | 280~340 | 200~260 | |